

MANAGERIAL ACCOUNTING BREAK EVEN POINT FORMULA REGISTRATION
Registration with the SEC does not imply a certain level of skill or training. What effect will a simultaneous change in price, cost, and volume have on profits?Ĭontent sponsored by Carbon Collective Investing, LCC, a registered investment adviser.How will the change in sales mix in the context of a multiproduct firm affect profits?.What effect will changes in fixed and variable costs have on profits?.What is the minimum level of sales needed to avoid losses?.What sales volume is required to produce the desired profits?.Importance of Break-Even Point Analysisīreak-even point analysis can be applied to answer many important questions in business, including: The break-even point or cost-volume-profit relationship can also be examined using graphs. Graphical Presentation Method (Break-Even Chart or CVP Graph) If the same cost data are available as in the example on the algebraic method, then the contribution is the same (i.e., $16). Budget Total Basisīreak-even point = Total fixed cost X (Sales / Contribution margin) Now, calculate the break-even point in dollars using the following formula:īE point (dollars) = Fixed cost / CM (expressed as a percentage of sales revenue) Use the following formula to calculate the break-even point in sales units: Let's consider the same figures for ABC Limited used in our example on the algebraic method. It is also possible to compute the break-even point using the contribution margin method. Contribution Margin Method (or Unit Cost Basis) To do this, we use the following equation:īE point in dollars = BE point in units x SP Now, as we have calculated the break-even point in unit terms, we can easily compute the break-even point in dollars. Where Y is the number of units sold to break-even. The following formula can be used to calculate the sold number of units at the break-even point: Required: Calculate the break-even point in units and dollars using the algebraic method. The different costs per unit are as follows: Suppose that ABC Limited manufactures and sells a single product. Using the algebraic method, we can also identify the break-even point in unit or dollar terms, as illustrated below. With this in mind, the following equation can be used to find the break-even point (o): The following equation is helpful when finding the break-even point using the algebraic method: This section provides an overview of the methods that can be applied to calculate the break-even point. Profit = (Unit sales price x Sales volume in units) - (Unit variable cost x Sales volume in units) - Fixed costs M ethods to Calculate Break-Even Point This equation can be restated as follows:
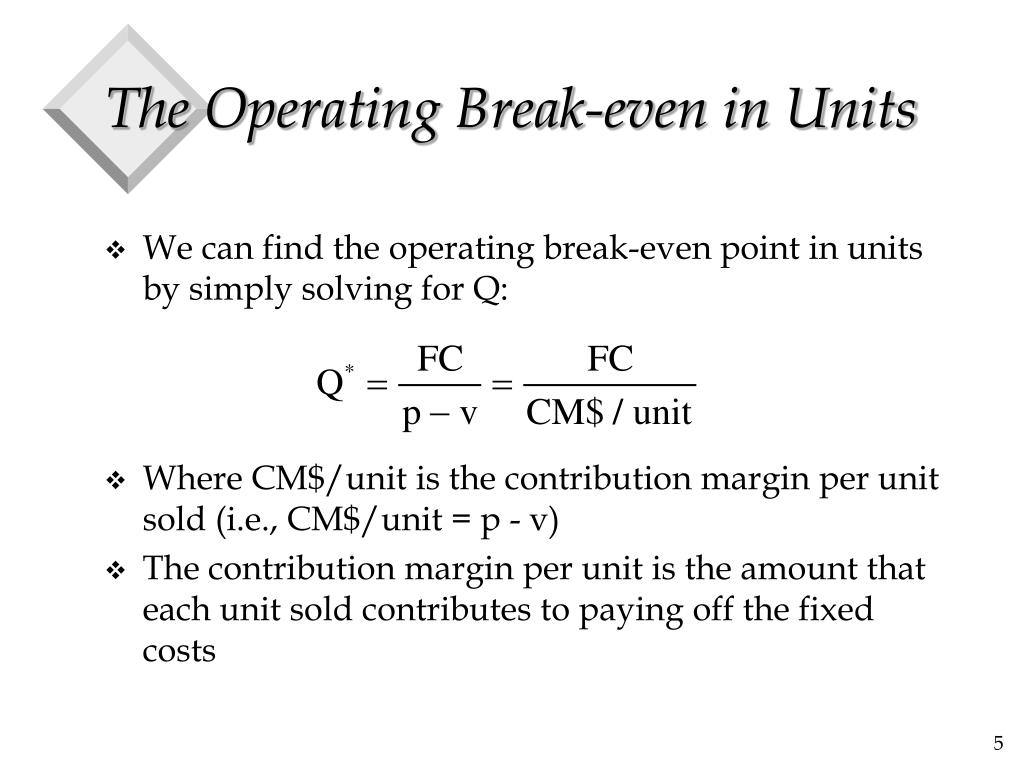
Where the sales revenue at break-even point = Fixed cost + Variable cost Profit = Sales revenue - Variable costs - Fixed costs Formula For Break-Even PointĪs you will be aware, profit can be calculated as sales revenues minus costs, where costs are either variable or fixed. Sales below the break-even point mean a loss, while any sales made above the break-even point lead to profits. In other words, the no-profit-no-loss point is the break-even point. The basic objective of break-even point analysis is to ascertain the number of units of products that must be sold for the company to operate without loss. It is possible to calculate the break-even point for an entire organization or for the specific projects, initiatives, or activities that an organization undertakes. This point is also known as the minimum point of production when total costs are recovered. The income of the business exactly equals its expenditure. The break-even point is the point at which there is no profit or loss.Īt the break-even point, the total cost and selling price are equal, and the firm neither gains nor losses. The activity can be expressed in units or in dollar sales. The break-even point is the volume of activity at which a company's total revenue equals the sum of all variable and fixed costs.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
